LAMP is a free and open-source stack made up of four software Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB and PHP. Linux is used as an operating system, Apache is used as a web server, MariaDB used for database and PHP used as a language. It is commonly used for hosting website and deploying high-performance web apps on Linux environment.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to install LAMP server and secure it with Let’s Encrypt free SSL on CentOS 8 operating system.
Prerequisites
- A server running CentOS 8.
- A root password is configured on your server.
- A valid domain name is pointed to your server IP address.
Getting Started
By default, SELinux is enabled in CentOS 8 server. So you will need to disable it first.
You can do this by editing /etc/selinux/config file:
nano /etc/selinux/config
Make the following changes:
SELINUX=disabled
Save and close the file. Then, restart your server to apply the changes.
Install Apache Web Server
By default, Apache is available in the CentOS 8 default repository. You can install it by running the following command:
dnf install httpd
Once the installation is completed, start httpd service and enable it to start after system reboot by running the following command:
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd
Now, open your web browser and type the URL http://your-server-ip. You will be redirected to the Apache default page as shown below:
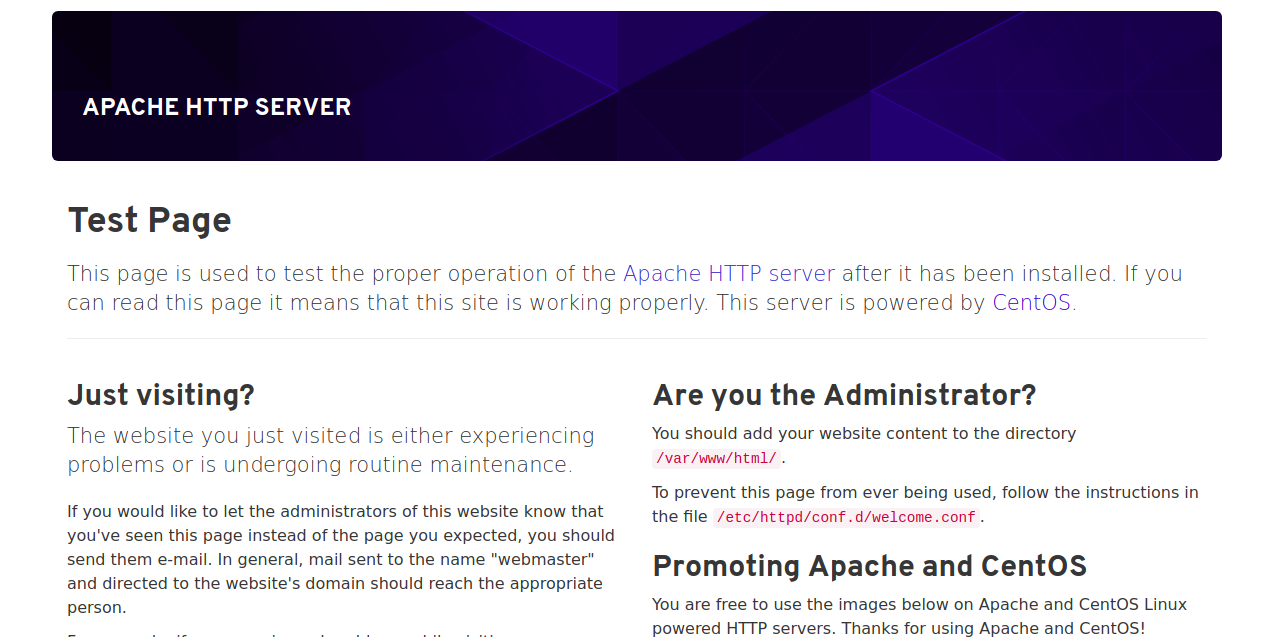
That means Apache web server is working fine.
Install MariaDB Database Server
MariaDB is used as a database server. You can install it by running the following command:
dnf install mariadb-server
Once installed, start the MariaDB service and enable it to start after system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start mariadb systemctl enable mariadb
By default, MariaDB server is not secured. So you will need to secure it first. You can secure it with the following command:
mysql_secure_installation
Answer all the questions as shown below:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Set root password? [Y/n] n Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Once secured, you should get the following output:
Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB!
Install PHP
By default, PHP is available in the CentOS 8 default repository. You can install it by running the following command:
dnf install php php-cli php-mysql php-curl php-gd php-zip
Once all the packages are installed, open php.ini file tweak some recommended settings:
nano /etc/php.ini
Change the following lines:
memory_limit = 256M max_execution_time = 300 upload_max_filesize = 100M post_max_size = 128M date.timezone = Asia/Kolkata
Save and close the file. Then, restart httpd service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart httpd
Create a Virtual Host for Your Domain
Next, you will need to create a virtual host configuration file for your domain example.com. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@example.com
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
ServerName example.com
DirectoryIndex index.html
ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/example.com.error_log"
CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/example.com.access_log" common
</VirtualHost>
Save and close the file.
Next, create a sample index page for your domain:
nano /var/www/html/index.html
Add the following lines:
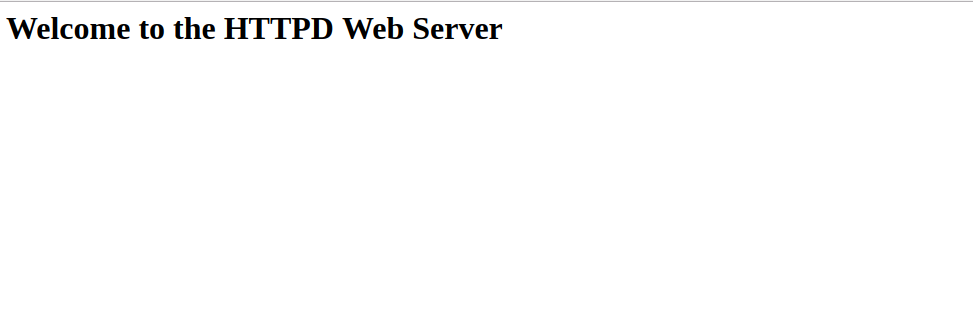
<html> <h1>Welcome to the HTTPD Web Server</h1> </html>
Save and close the file. Then, restart httpd server to apply the changes:
systemctl restart httpd
Now, open your web browser and type the URL http://example.com. You will be redirected to the following page:
Secure Apache with Let’s Encrypt
Your Apache web server is now installed and configured. Now, you will need to secure your domain with Let’s Encrypt free SSL.
First, you will need to install Certbot Let’s Encrypt client to download an SSL certificate. The certbot package is not available in the CentOS 8 package repository. So you will need to download it from the Certbot official website.
You can install it with the following commands:
wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto mv certbot-auto /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto chown root /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
Now, run the following command to obtain and install an SSL certificate for your domain.
certbot-auto --apache -d example.com
You will be asked to provide an email address and agree to the terms of service. You will also need to choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS. Please select the appropriate option and hit the Enter. Once the installation is successfully finished, you should get the following output:
IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2019-08-14. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Set Up Automatic Renewal
Let’s Encrypt certificate is valid for 90 days. So it is recommended to renew the certificate before it expired. You can set up the Cron job to renew the certificate automatically.
To do so, create the crontab with the following command:
crontab -e
Add the following line:
0 0,12 * * * root python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto renew
Save and close the file, when you are finished.
Congratulations! your example.com domain is now secured with Let’s Encrypt free SSL.