As a Linux system administrator, it is a challenging task to closely monitor system resources. With detailed knowledge of the system, users can take appropriate action in the event of changes to system resources or problems during process execution. There are various tools for monitoring all system/server resources in the Linux environment. BpyTOP is one of the most popular terminal-based tools for managing system resources such as memory, disks, networks, processors and system processes. Users who use the bashtop utility can use the same functions in BpyTOP. BpyTOP is written in Python and has a game-inspired theme. The tool is a port of bashtop and supports macOS, GNU/Linux and FreeBSD. In this article we will show you how to install the system resource monitoring tool bpytop on the Ubuntu 20.04 system using all possible methods.
Installing the BpyTOP on Ubuntu
BpyTOP can be installed on the Ubuntu 20.04 system using various methods:
- Install BpyTOP via the Ubuntu repository
- Install BpyTOP via the Python PIP
- Install BpyTOP by compiling from source code via the Git repository
- Installing BpyTOP with the snap application
Today we will discuss all the methods for installing the BpyTOP tool on the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system. Let’s go through each method in detail!
Installing the required module dependencies
Launch the terminal window with the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl+Alt+t”. Log in as root user on the Ubuntu system and install the required modules “python3” and “Psutil module”. Python3 is already pre-installed on most Ubuntu distributions. So check the installed version by executing the command below:
$ python3 --version
![]()
Now install the “psutil module”. This module can be installed with the python-pip tool. Install the “psutil” module by executing the command below:
$ pip3 install psutil
Once all required modules are installed on Ubuntu 20.04, install the resource monitoring program BpyTOP on your system.
Method 1: Install BpyTOP via the package manager
The BpyTOP tool is not included in the official Ubuntu apt repository. However, if you add the external Debian repository Azlux, you can install the BpyTOP resource monitoring program on Ubuntu/Debian distributions. Therefore, add the Azlux repository and download the repository’s GPG key to your system by executing the command below:
$ echo "deb http://packages.azlux.fr/debian/ stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/azlux.list
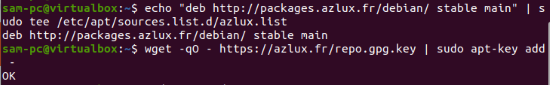
$ wget -qO - https://azlux.fr/repo.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
![]()
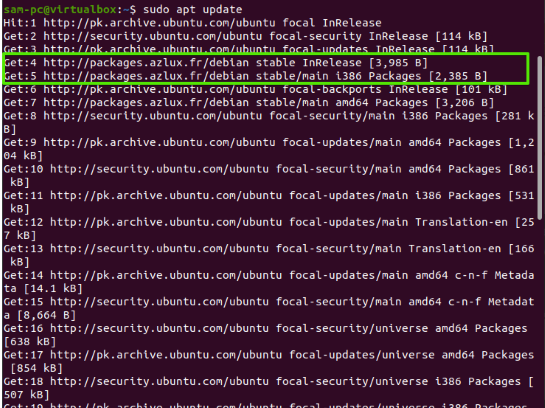
After adding the Azlux repository, update the apt package list by running the following command:
$ sudo apt update
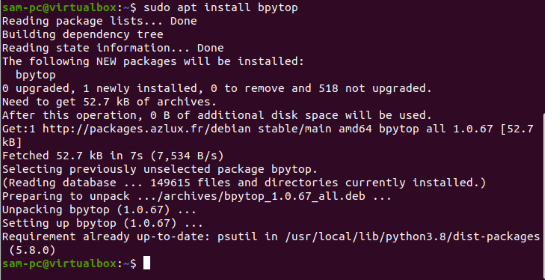
Now install the BpyTOP tool using the command below:
$ sudo apt install bpytop
Method 2: Install BpyTOP with the Python PIP
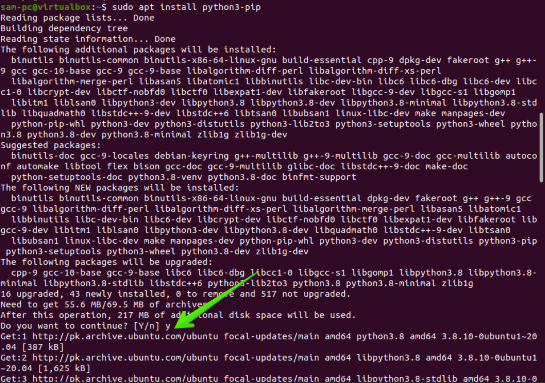
Another method to install BpyTOP is to use the pip library. Therefore, install pip by executing the command given below:
$ sudo apt install python3-pip
After the installation of pip3 is complete, install the BpyTOP tool using the python-pip module as follows:
$ sudo pip3 install bpytop
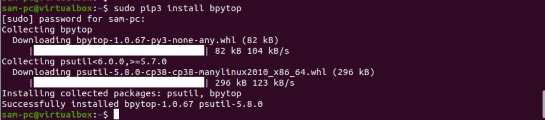
Check the installed BpyTOP version by running the following command:
$ BpyTOP --version

Method 3: Installing BpyTOP by compiling from source using the git repository
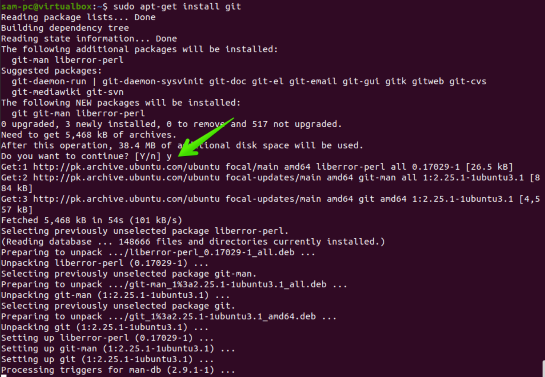
Sometimes Linux users prefer to use the Git repository to install the software. In this case, the BpyTOP tool can be installed on your Ubuntu system by compiling the source code with the Git repository. First, make sure that the Git tool is installed on your Ubuntu system. Otherwise, you can install it by executing the command below:
$ sudo apt-get install git
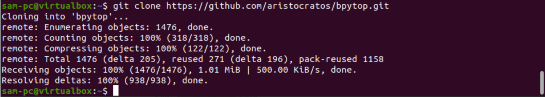
Then clone the package using the Git repository from Github. The following commands will show you how to install the BpyTOP utility via the Git repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/aristocratos/bpytop.git
Navigate to the BpyTOP directory and install the packages using the command below:
$ cd bpytop $ sudo make install
![]()
Method 4: Install Byptop with the Snap application
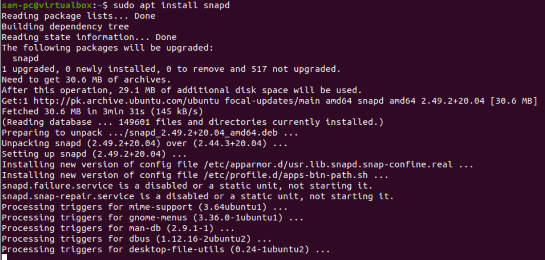
You can also use the snap application to install the BpyTOP tool on the Ubuntu 20.04 system. So install the snapd package and then install the BpyTOP utility by running the command below:
$ sudo apt install snapd
$ sudo snap install bpytop
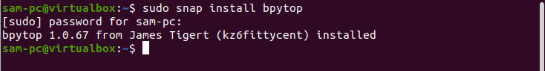
Remove / Uninstall BpyTOP Tool from Ubuntu 20.04 System
If you no longer need the BpyTOP tool in the Ubuntu 20.04 environment, you can simply uninstall it to free up space on your system.
If BpyTOP was installed with the package manager, you can uninstall it with the following command:
$ sudo apt purge --remove bpytop
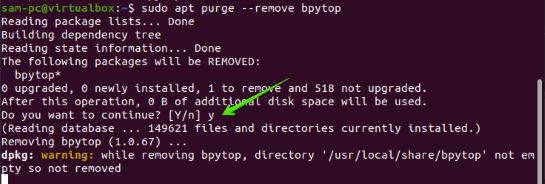
Remove the associated repository from your system as follows:
$ sudo rm -rf /etc/apt/sources.list.d/azlux.list
Remove the package via Snap:
$ sudo snap remove bpytop
Uninstall BpyTOP with pip:
$ sudo pip3 uninstall bpytop
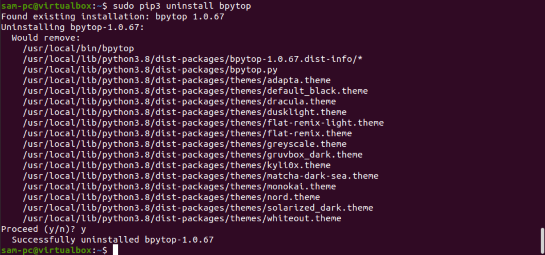
Using the BpyTOP Resource Monitoring Tool
Enter the command BpyTOP in the terminal to start the user interface as follows:
$ bpytop
The following BpyTOP user interface will be displayed in the terminal window, where you can view details about the CPU, memory and running process, etc.
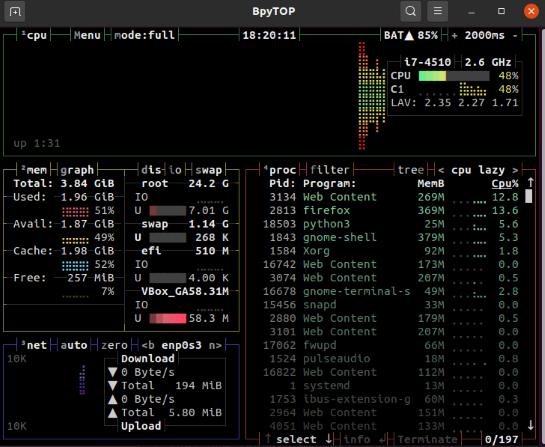
Press “Esc” to switch to the main menu and the following options will be displayed on the interface:
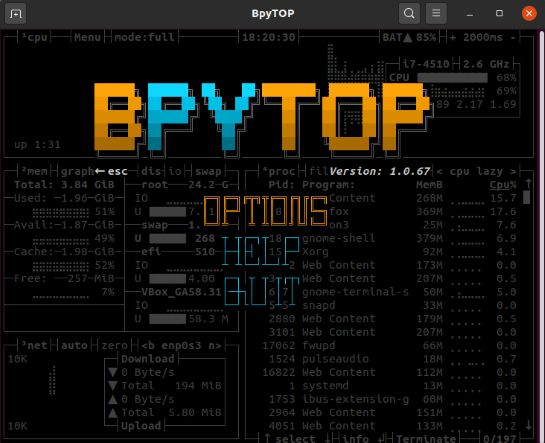
Click “Options” and the following settings will be displayed in the BpyTOP window:
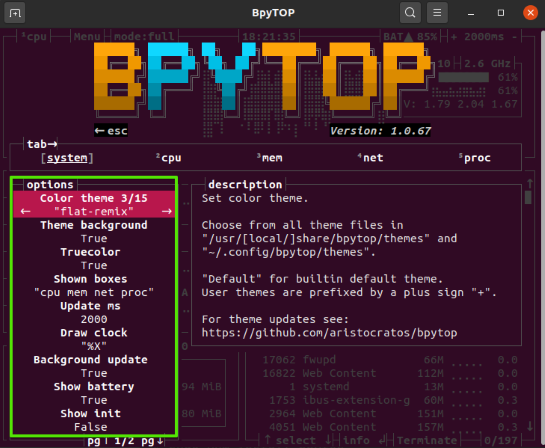
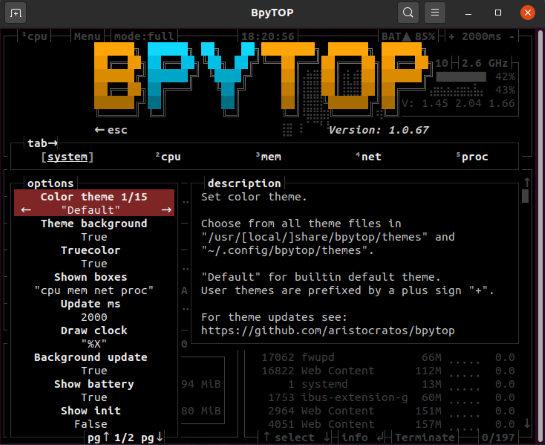
In the screenshot above, you can change the highlighted options. For example, we want to change the default theme of the user interface. Click on the forward arrow and set the desired theme as follows:
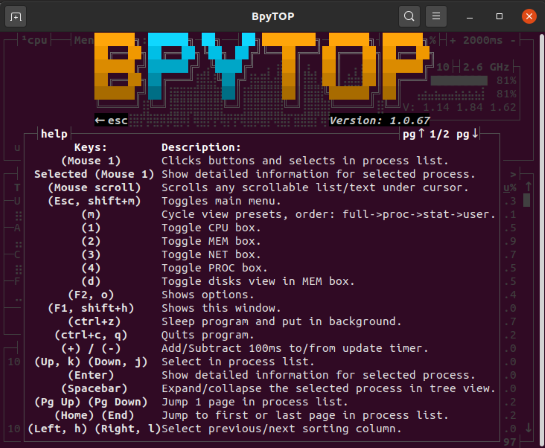
Press “Help” again and the following settings will be displayed on the BpyTOP interface:
Conclusion
That’s it for the Bpytop demo. We have installed the resource monitoring tool bpytop on the Ubuntu 20.04 distribution via the command line. We also discussed the steps to uninstall bpytop in all possible ways. Now I hope you can install and use the bpytop tool on the Ubuntu system by using any of the above methods. With the bpytop tool, the system administrator can easily monitor all system resources. You can find more help on installing the bpytop tool on GitHub.