Rust is often called rust-lang. Rust is a general-purpose programming language that aims to be safe, concurrent, and practical.
Rust was created by Graydon Hoare in 2010, and the first stable version (1.0.0) was released in May 2015. Graydon Hoare has been the principal architect of Rust, with contributions from Dave Herman, Brendan Eich, and others. Rust is free and open-source software sponsored by Mozilla Foundation.
Rust can be written as a low-level language geared towards creating an OS and various other tools, or as a higher-level language to create “ordinary applications”. There are two primary use cases for Rust:
Embedded programming – Creating very small software such as microcontrollers. Low-level system programming – Creating operating system kernels and embedded systems that need to manipulate hardware directly.
Rust has some similarities with both C++ and Python, and the syntax is influenced by these languages. There is also an increasing number of programming languages that borrow ideas from Rust’s type system. The main features of the language include: safety, speed, and concurrency (including async/await syntax like JavaScript).
Rust is a statically typed language with strong and static type checking. Static typing is the process of verifying the correctness of a program at compile-time, as opposed to runtime. This means that Rust can catch errors in your code before it’s even run. Static typing also allows Rust to generate faster code, as all types are known at compile time.
Rust has two main features that set it apart from other languages: borrowing and lifetimes. Borrowing means that a variable can be assigned a value only once and must be returned to the original owner when no longer needed. Lifetimes define how long a borrowed value is valid. This prevents memory leaks and helps ensure data safety.
This guide will show you how to install Rust on AlmaLinux 8, an easy-to-use Linux distribution for embedded systems and the Internet of Things. You will have the most recent stable version of Rust on your system after following these instructions.
Prerequisites
In order to follow this guide, you will need to have
- Root access to your AlmaLinux installation.
- A server with AlmaLinux 8 installed.
Updating your system
First, make sure your system is up to date by running the following command.
sudo dnf update
Next, run the command below to install the EPEL repository. EPEL is Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux. EPEL provides high-quality add-on packages for the Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution.
sudo dnf install epel-release -y
Next, you need to install the cmake, gcc and make packages.
Cmake is a tool that is used to control the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler-independent configuration files,
Gcc (GNU Compiler Collection) is an integrated suite of toolsets that support all stages of work with source code on Linux/Unix platforms. Make is a tool that automatically builds computer programs.
sudo dnf install cmake gcc make -y
Installing Rust
Now you have everything you need to install Rust. Run the following command to download and install Rust.
Curl is a command-line tool for transferring data with URL syntax. This guide assumes that you have curl installed, but the installer will automatically install it if you don’t.
The command below installs version 1.24 of rustc, and sets this version as your default Rust compiler. If you do not want to use this particular version for whatever reason, feel free to specify another version after curl.
https://sh.rustup.rh is a secure shell (ssh) link which will direct rustup.rs to the latest Rust installation script.
The sh command executes the contents of the file specified after it. In this case, the Rust installation script will be downloaded and executed.
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
You will see a few questions about your preferences and environment. The most important question is whether you want to make Rust your default compiler. If you choose yes, Rust will be automatically invoked whenever you run gcc, make, or any other tool that requires a compiler.
Enter 1 and press Enter to proceed with the installation.
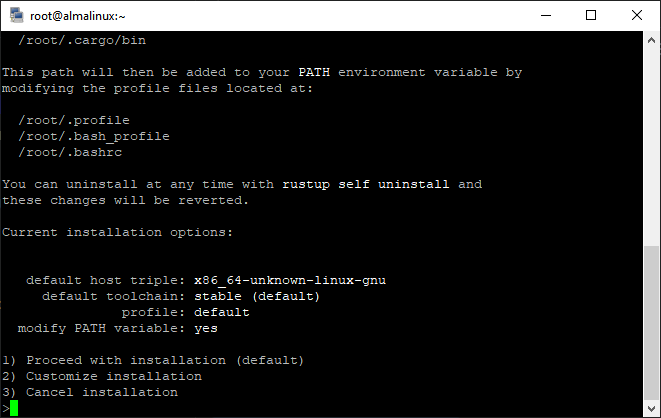
Once you press Enter, the installation will begin. t may take a few minutes to complete, so be patient.
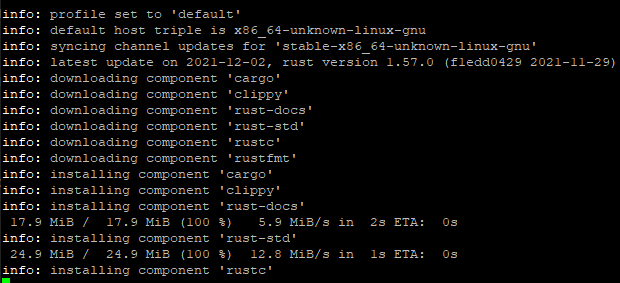
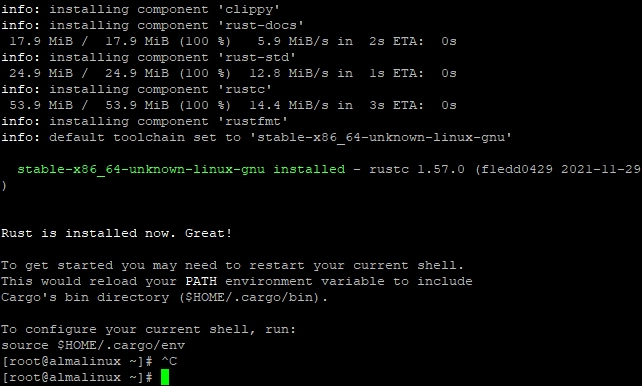
Now, run the source ~/.profile command to reload your bash profile and ensure that Rust is installed properly. Source is a command that tells bash to read the contents of the file specified after it. In this case, the .profile file will be read, and any changes made to it will take effect.
source ~/.profile
Next, run the source ~/.cargo/env command to set up your environment variables. The source ~/.cargo/env command allows you to automatically run the correct version of Rust for whatever directory you are in, provided that it has been installed into your path.
source ~/.cargo/env
To verify that Rust is installed correctly, run the following command. Rustc is a Rust compiler.
rustc -V
Output like this should pop up. The output confirms that Rust is installed and configured correctly.

Creating a Rust Sample Project
Now that you have Rust installed, you can create a new project. In this tutorial, we will create a simple “Hello World” program to test the installation before moving on to more complicated code.
To do that, first navigate to your home directory where your new project to be stored using the cd command. Now, run the mkdir to create a new directory called hello_world and move into your newly-created directory.
cd && mkdir hello_world && cd hello_world
Next, use the command below to create a new file called helloworld.rs using the nano text editor. You can use any text editor as long as it works on the Linux platform.
sudo nano helloworld.rs
Inside this file, copy and paste the following code.
fn main() {
println!("Hello World, this is a test provided by osnote.com");
}fn main() { is a keyword in Rust that denotes the beginning of a function.- println!(“Hello World, this is a test provided by osnote.com”); is a Rust macro that prints the string specified after it.
- } tells the compiler that the program has ended.
Save and close the file using Ctrl+X, then press Y to confirm the changes. Now, run the following command to compile your program into a binary file that can be executed from the terminal.
We will run the rustc compiler directly with the file name. Since you installed Rust, it should be accessible in the path.
rustc helloworld.rs
If everything went successfully, the helloworld executable file should have been created in the same directory where your helloworld.rs source code is located. Run the command below to list all the files in the directory.
ls
Sample output:
![]()
Run the following command to run your helloworld program.
./helloworld
You should see a message that looks something like this. Congratulations! You have successfully installed Rust on AlmaLinux 8 and created your first Rust program.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we showed you how to install Rust on AlmaLinux 8 and demonstrated the process of creating a simple “Hello World” program.
For more information about Rust or programming in general, please check out its extensive documentation.
Thank you for reading! We hope this article was helpful and that you will enjoy learning to program with Rust.